Managing costs in BeCPG
The different types of costs
The cost management module in beCPG can be used to calculate the cost of products, taking into account, for example:
- RM costs
- PACK costs
- Fixed costs
- Production costs
These costs can be :
- Formulated: calculated from the cost of raw materials or packaging
- Manual: added at Finished Product or Semi-Finished Product level.
You can change the cost to manual by ticking the manual box when creating the cost in the administration, or by directly modifying the Manual column in the product cost list.

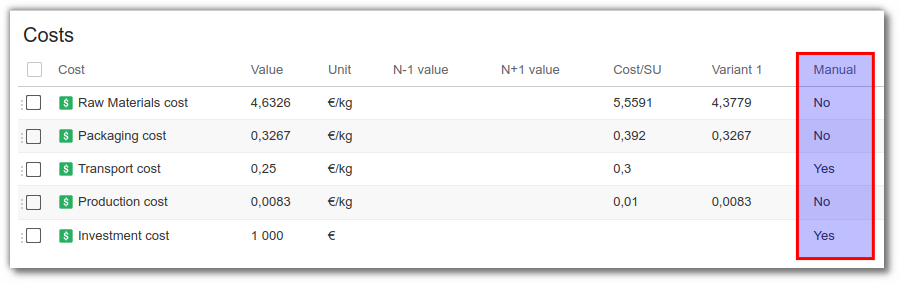
Costs in BeCPG
To obtain the total cost of a finished product, you can add different types of cost. To create a cost, you can refer to Administration beCPG
Raw material costs (RM)
In the raw material Costs list, add the "Raw Materials cost":
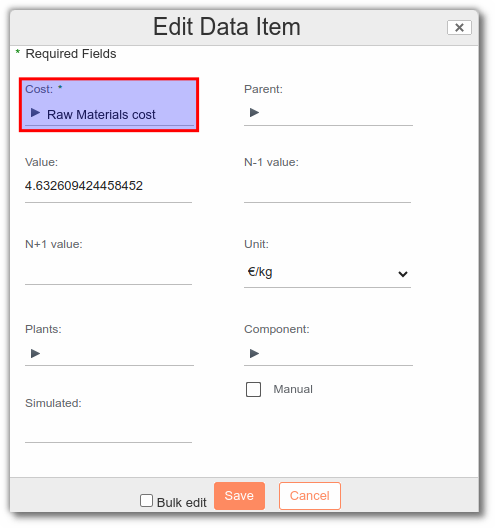
- The Value field refers to the current cost, which will be used in subsequent cost calculations.
- The N-1 Value field refers to the previous year's cost.
- The N+1 Value field refers to the cost for the following year.
- The Unit field is used to select the unit associated with the cost.
- The Factory field is used to select the factories from which the product comes.
- The Component field is used to associate the cost with a particular entity.
Packaging costs (PACK)
In the packaging Cost list, add the "Packaging cost":
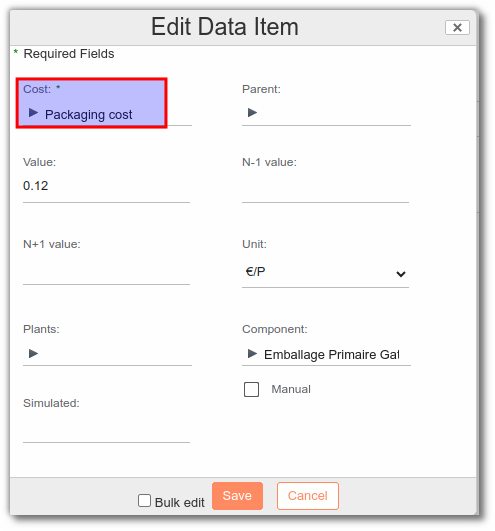
For more information on packaging, go to the following link Packaging management.
Example of a calculation using BeCPG software:
- Primary Pack = 0.12€/Piece; I can put 1 product per Primary Pack. My Primary Pack cost is 0.12€/Sales Unit (SU).
- Secondary Pack = 1,32€/Piece; I can put 10 products in my Secondary Pack. My Secondary Pack cost is 0.132€/SU.
- Tertiary Pack = €16.92/piece; I can put 250 products in my Tertiary Pack. My Tertiary Pack cost is 0.06768€/SU. Therefore my total packaging cost is €0.31968/SU.
Transport costs
Transport costs can be added to raw materials or finished products. If you are managing 2 costs (RM & FP), remember to create a separate cost for each type of transport. e.g. RM Transport Cost vs FP Transport Cost.
For Raw Materials
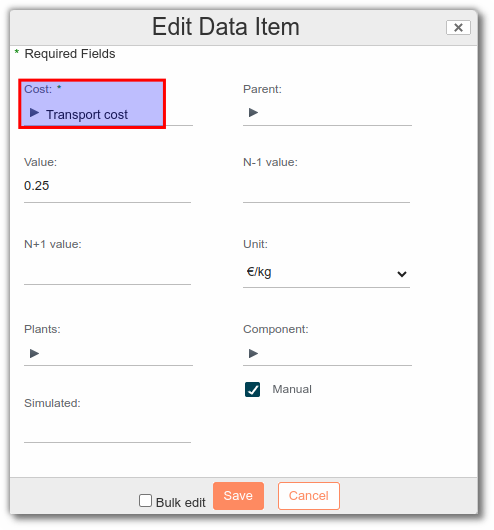
This represents the cost of transport for raw material to plants for example. Add the Transport cost to the raw material level:
For Finished Product
This is the cost of transporting the finished product to distributors or the point of sale. Add the Transport cost to the finished product level.
Note: Put transport costs in manual. Otherwise, the field will be overwritten and the information lost during formulation.
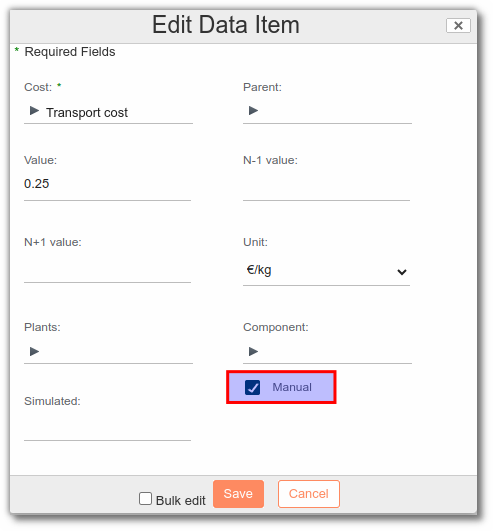
Calculation example: If it costs me 100€ to transport my 4000kg of raw materials to the plants, the cost of transport is 0.025€/kg.
Production costs
Production costs include, for example:
- energy used (electricity, gas, etc.)
- resources (washing water, etc.)
- equipment (production line, etc.)
- operators
To set up a resource, refer to the following page: Process management
In the Resources Cost list, add the "Production cost":
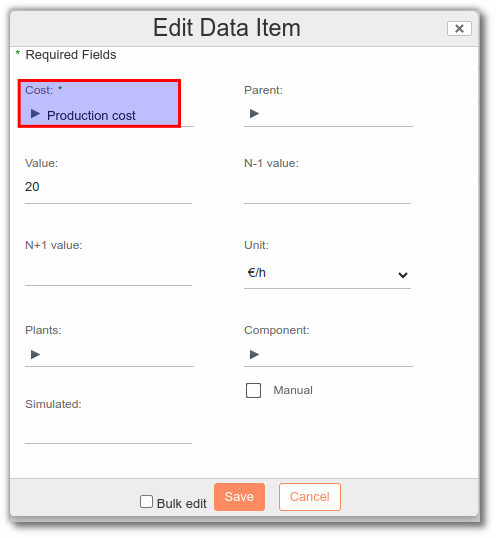
Note: In the "Process list" tab of the Finished Product, the user can add a rate to the production line.
Calculation example: Here, our production line costs €20/hour to operate. My production line has a production rate of 2000 P/h at 20€ per hour. This gives us a production cost of €0.01/SU.
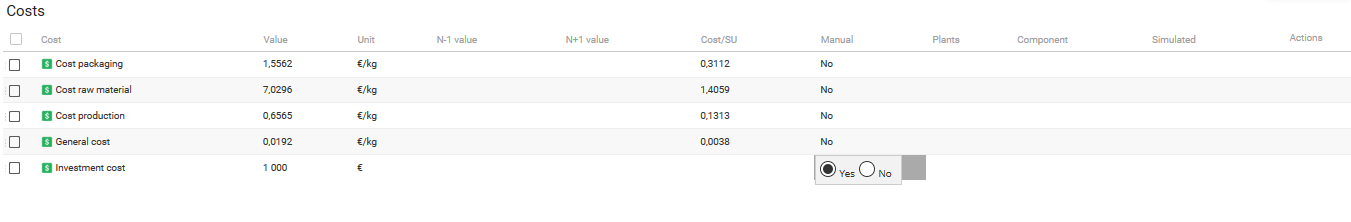
Investment costs
In the finished product costs list, it is possible to add the Investment cost. This is a manual cost, i.e. it does not depend on the quantity of the product (example: Design). To add an investment cost, the user can create a new characteristic in beCPG Administration
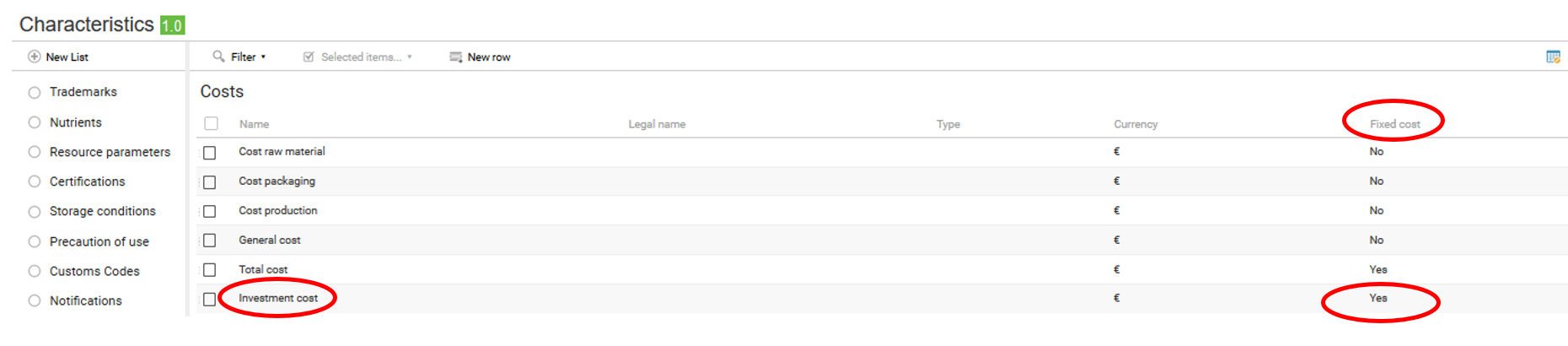
When investment costs are created in the entity (FP, RM, ...), they must be in manual. Otherwise, during formulation or simulations, the box will be overwritten and the information lost.
In the Finished Product cost list , it is possible to add the Investment cost. This is a manual cost, i.e. it does not depend on the quantity of the product (example: Design).
Finished Product total cost
To view the total cost of a Finished Product, users must ensure that they have completed the following lists:
- Composition: ensure that all the RMs are present, the shrinkage completed if there is any and their costs completed.
- Packaging: ensure that all packaging is present and their costs have been completed.
- Process list: ensure that the various resources are present and that their costs are complete.
In the finished product cost tab, add the desired costs to the list:
- Raw materials: RM cost
- It is important to complete the Loss % in the FP Composition tab. Loss % has a direct impact on the cost of the FP.
- Packaging: PACK cost
- It is important to complete the Loss % in the Packaging tab of the FP. Loss % with a direct impact on the cost of the FP.
- Transport: Transport cost
- Production: Production cost
The formulated costs will be calculated automatically. If no cost has been entered in the RM, packaging or resources, the line will return an empty value.
The user can view the total cost/SU on the right of the page under the name Cost per SU.
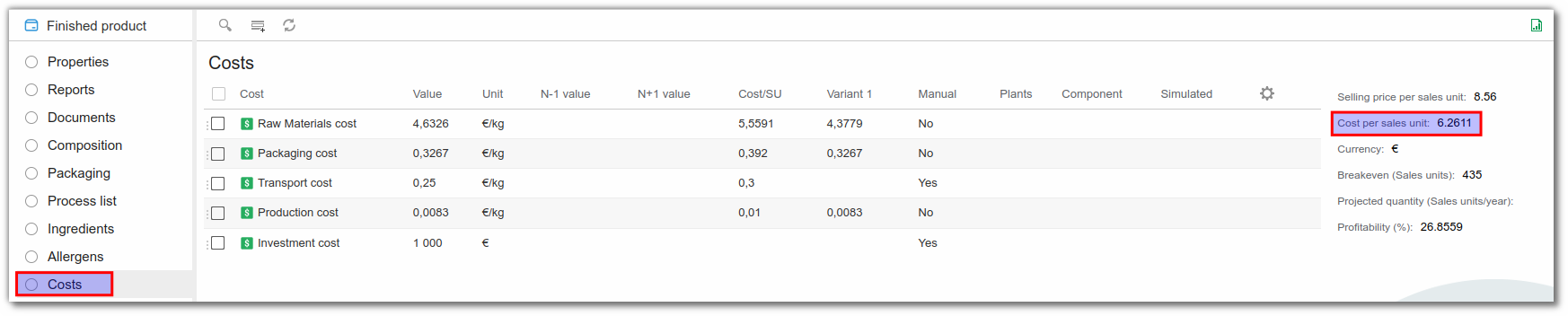
The user can also add the selling price per SU to obtain the product's profitability.
If a cost is missing from the drop-down lists, refer to beCPG Administration to create it.
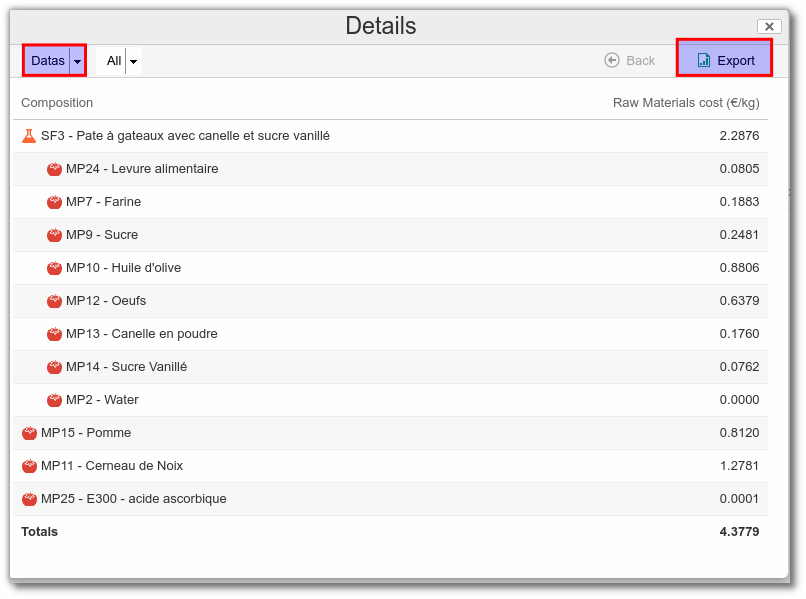
View detailed costs
Details
Select the "Costs" list. To view the details of a cost, click on the "..." to the right of your line, then on "Show Characteristic Details".
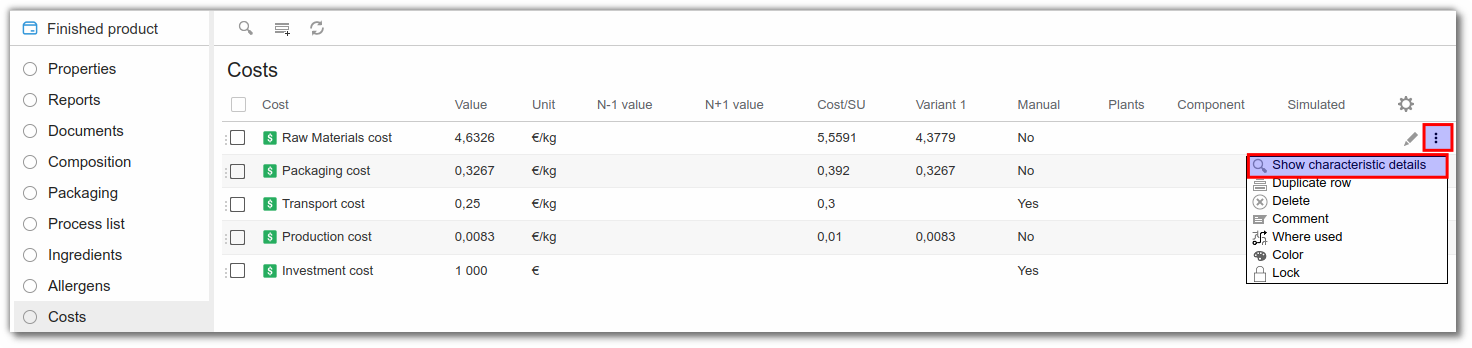
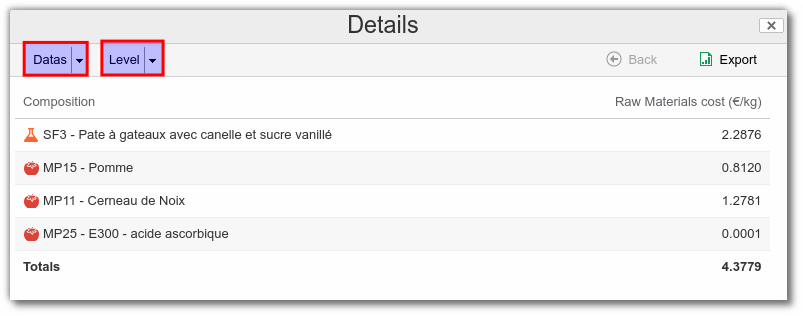
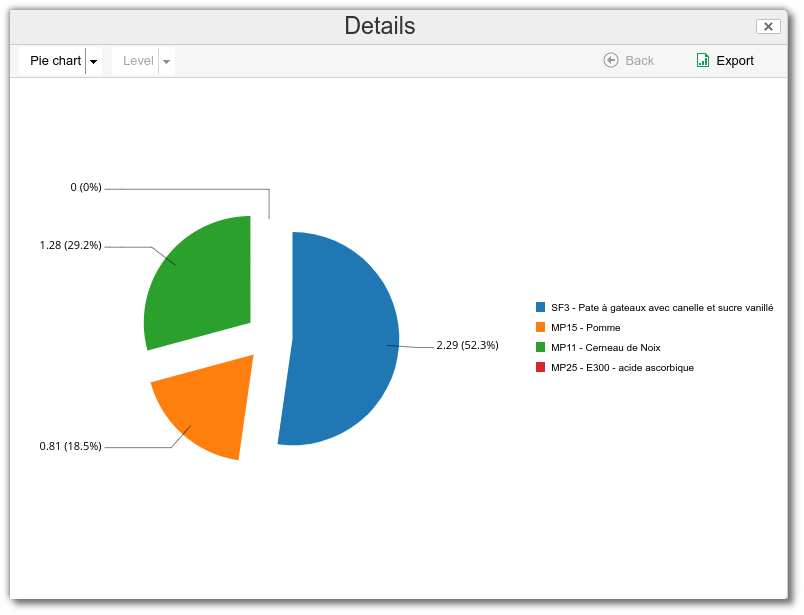
The user can then choose :
- the type of graphical representation.
- the level of detail to be displayed (only available for the Datas display).
Cost reports
Cost reports can be created in the "Report" list. The user can select "Cost sheet" in the desired language (english in that case).
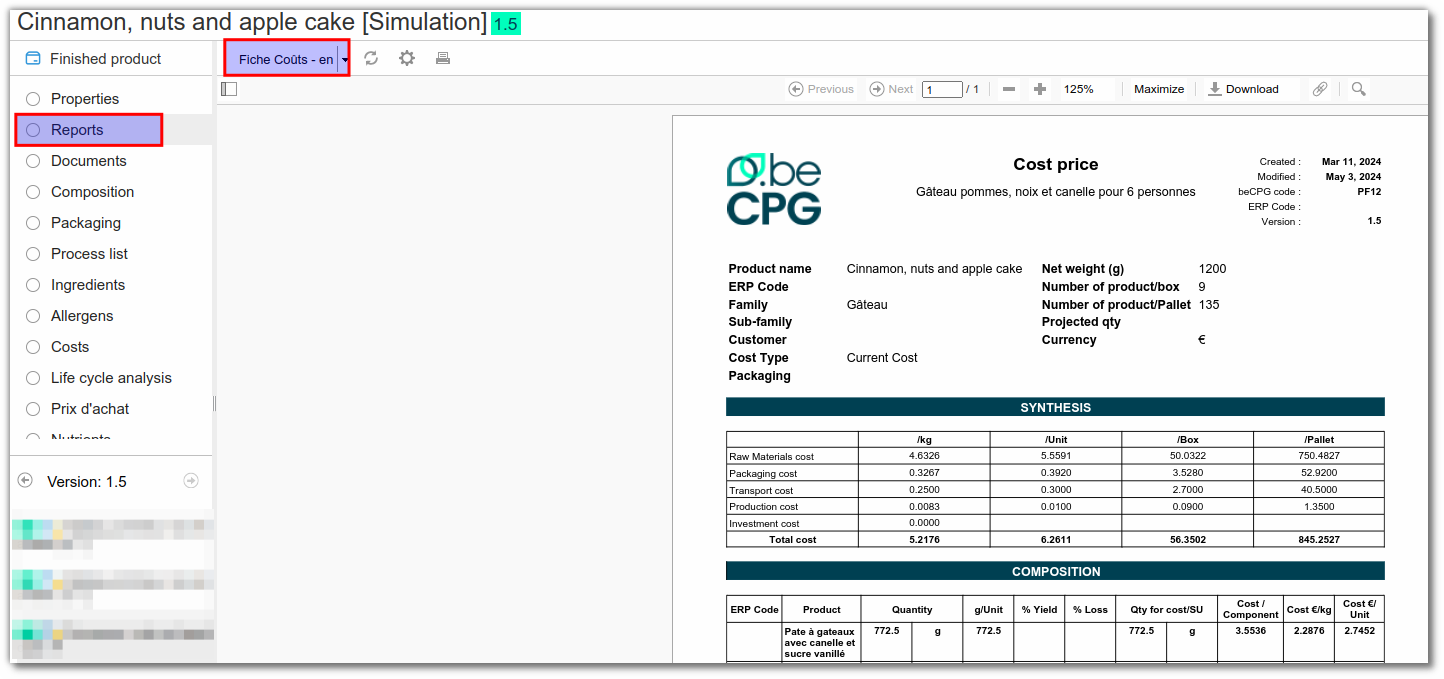
Data can be exported so that it can be viewed in a document. It is recommended that you use the graphical representation Data Table and the desired level of detail.
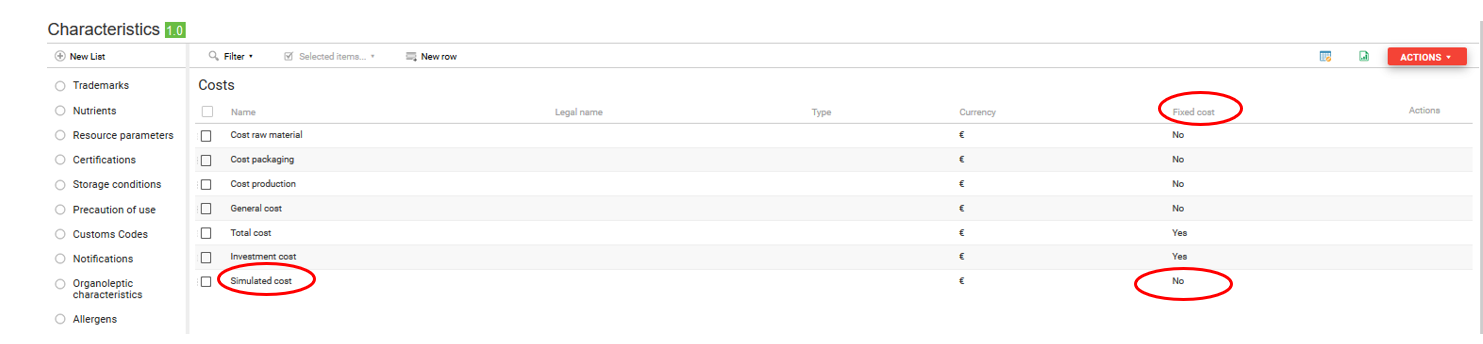
Cost change simulation (simulated costs)
In beCPG, it is possible to add a simulated cost to a given cost. In other words, it is possible to simulate a price change and see its impact on the final cost (e.g. change of supplier, etc.) without modifying the entity values (SF, RM, etc.).
If the simulated cost does not exist, create a new characteristic in BeCPG administration cf: BeCPG administration
Back in the entity (SF, FP, ...), we create a simulated cost to which we assign the desired cost as parent. To add a simulated cost :
- In the Finished or Semi-Finished Product cost tab: add the simulated cost with the impacted cost as its parent and complete the following fields
- Parent: What cost will the simulated cost impact.
- Component: the name of the component whose price is changing.
- Simulated: the new price of the component.
The unit will automatically take the value of its parent.
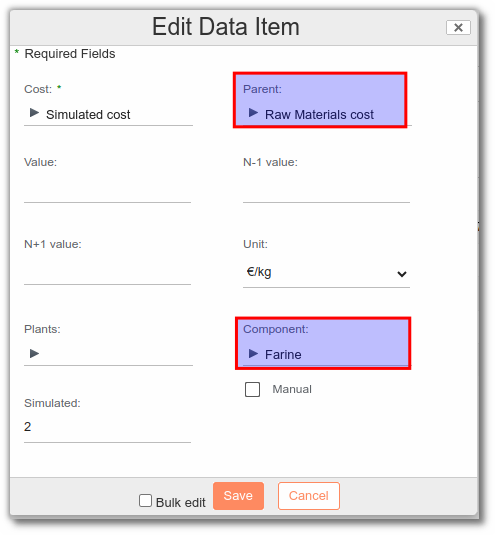
Example: the Simulated cost has been added to the Raw Material cost. The simulation cost has a Flour component and a Simulated value equal to 2€/kg.
The calculated cost displayed is the cost difference between the initial price and the simulated RM price (negative if cheaper, positive if more expensive).
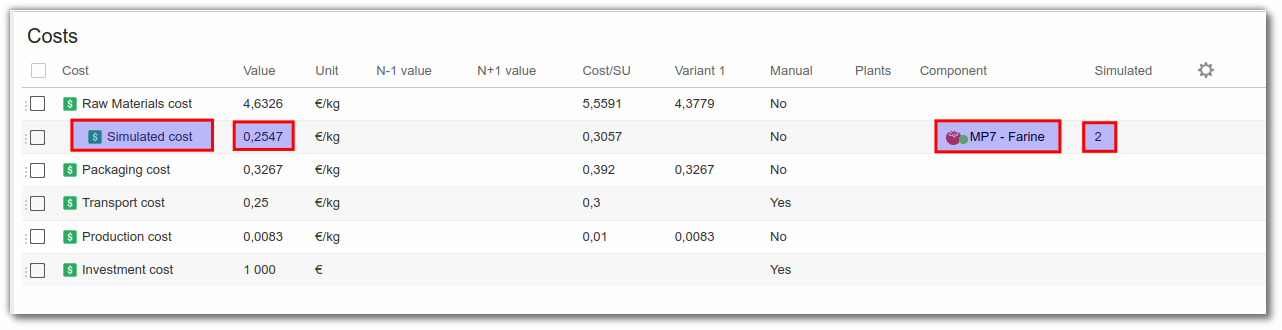
- You can change the value of the simulated cost directly in the appropriate box at any time.
- Several simulated costs can be added to a single cost.
- The user can also add comments, as shown below:

Note: After any change in costs, remember to formulate your product.
The purchase price list
The purchase price list is an advanced cost management list. It offers more possibilities than the standard cost list.
The purchase price list is to be completed on Raw Materials or Packaging.
- The user can add the purchase price list to the Raw Materials and Packaging models. To add lists, please refer to beCPG Administration.
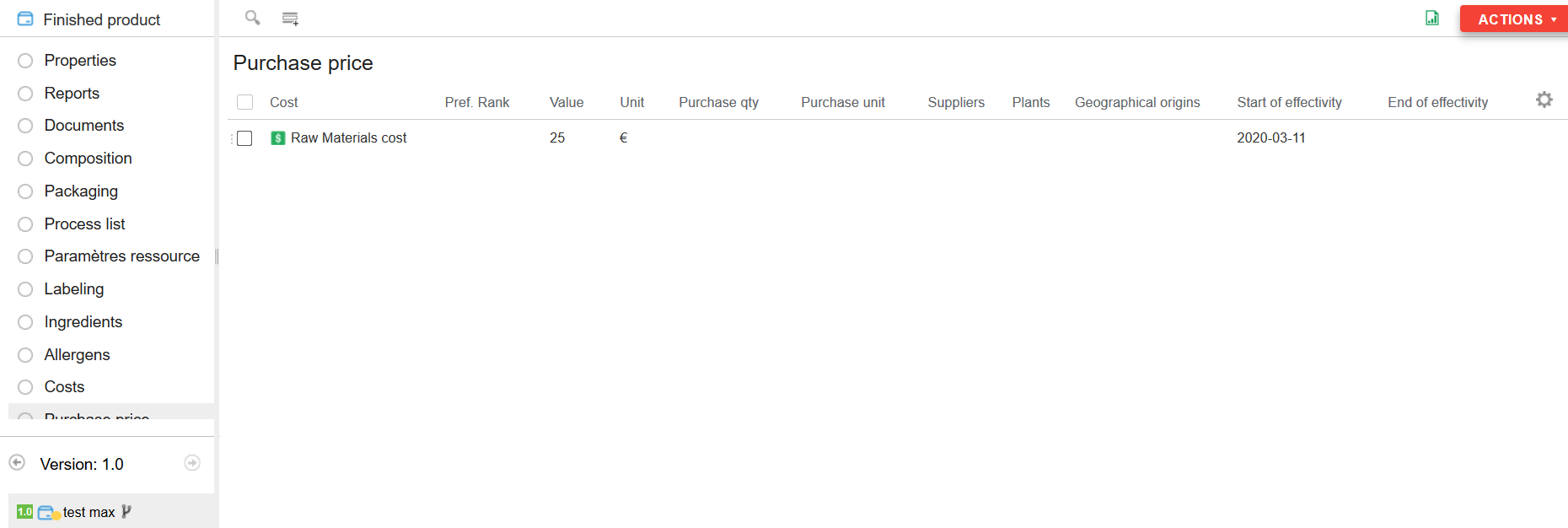
- The purchase price list works in the same way as the cost list with the addition of:
- Additional information:
- Plants
- Geographical origin
- Supplier
- Preference rank (optional): used if you have several lines in the purchase prices. Preference rank 1 is taken into account.
- Purchase quantity: used to keep a history of the various suppliers.
Effective date: date interval when the cost will be active. The user can only enter a start date if the cost has no scheduled end date.
On the Finished Products cost list, the RM and PACK cost is formulated according to the purchase price list if it is present.
Note: The purchase price list has priority over the cost list for raw materials and packaging.
When the purchase price list is present on an entity, there are several scenarios for formulating the costs of the entity that uses it:
- The purchase price list contains one or more costs that are also used by the cost list of the entity that uses it: the formulation of the cost list takes the purchase price list into account.
- The purchase price list is empty: the formulation takes the cost list into account.
- The purchase price list contains one or more rows with a rank less than or equal to 0: the formulation takes the cost list into account.
- The purchase price list contains only non-effective rows: the formulation takes the cost list into account.
- If the effective dates overlap, the preference rank is used.
- If several purchase price lines have the same effectivity rank greater than 0, BeCPG will smooth the purchase price in the cost list.