Ingredient management
beCPG offers a complete solution for tracing ingredients from raw materials to the finished product. More than just a list of ingredients, the list can be used to integrate essential data such as the biological and geographical origin of components, the presence of GMOs or ionizing elements, and other specifics required for labeling.
Ingredient management for raw materials
Raw materials are made up of ingredients. An ingredient is a component used in the preparation or manufacture of a product. There are several types of raw material, depending on their number of ingredients:
- Raw raw materials, made up of a single, generally natural, unprocessed ingredient (e.g. wheat, milk, fruit, vegetables)
- Intermediate raw materials, made up of a processed ingredient defined by regulations (e.g. flour, sugar, oil, concentrates).
- Compound raw materials, mixtures of raw ingredients (e.g. chocolate, fillings, ham).
Ingredients are managed at the raw materials level. To do this, select the “Ingredient” list, then “Add an item” and its characteristics:
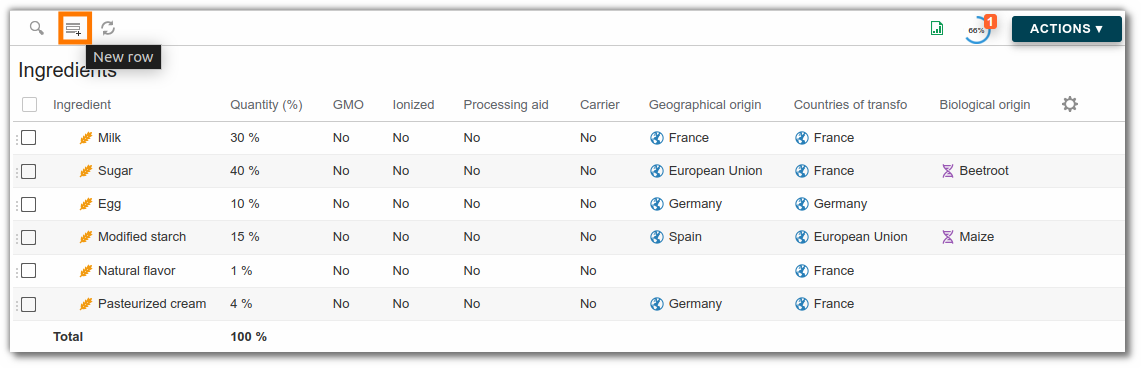
- Ingredient: the drop-down list corresponds to the ingredients available in the administration characteristics click here for more information.
- Quantity: The average percentage of the ingredient in the raw material.
- Mini : The minimum percentage of the ingredient in the raw material.
- Maxi : The maximum percentage of the ingredient in the raw material.
- GMO: To be ticked if the ingredient is a GMO (Genetically Modified Organism).
- Ionized: To be ticked if the ingredient is treated by ionization.
- Processing aid: To be ticked if the ingredient is considered as a technological auxiliary according to regulation (EC) no. 1331/2008.
- Carrier: To be ticked if the ingredient is considered as a support according to regulation (EC) n° 1333/2008.
- Geographical origin : Indicate the origin of cultivation of the ingredient, the drop-down list corresponds to the geographical origins available in the characteristics of the administration.
- Country of transfo : Indicate the ingredient's processing origin. The drop-down list corresponds to the geographical origins available in the administration characteristics.
- Biological origin: the drop-down list corresponds to the biological origins available in the administration characteristics.
- Claim: linked to the ingredient. (ex: EU organic agriculture).
- Additional information: allows you to add a complement to the legal label (*ex: ingredient = "aroma" and complementary information = "strawberry")
- Decl. Type:: as in composition, declaration types are available at ingredient level. Click here for more information.
- Alias: allows you to add alternative declarations to an ingredient. (e.g.: vitamin C, alias ascorbic acid). An ingredient can have 10 aliases, so when an ingredient is added to the mp, for example, 3 of the 10 aliases are locked. At the pf level, this allows you to choose (with the renaming rule) only from the 3 locked aliases. Aliases can be excluded from the search.
- Parent: Used for compound ingredients, it is possible to define a parent ingredient of other ingredients. (e.g.: in order to declare the components of a chocolate, it must be the parent of these ingredients). The detail can then be collapsed or un-collapsed to make long ingredient lists easier to read.
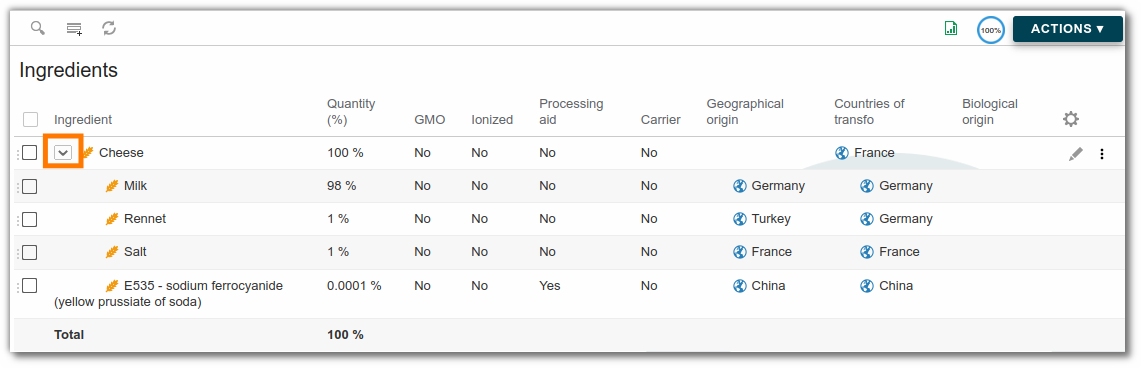
Total ingredients must equal 100%.
Modify or create an ingredient
Ingredients can be modified and created in the administration area. Click here for more information.
Ingredient formulation
Formulation will calculate the quantity of ingredients present in the product, based on the quantity of raw materials added to the composition and its list of ingredients. Click here for more information. Ingredients will be detailed flat except in the case of parent ingredient use, in which case the ingredients will remain grouped together.
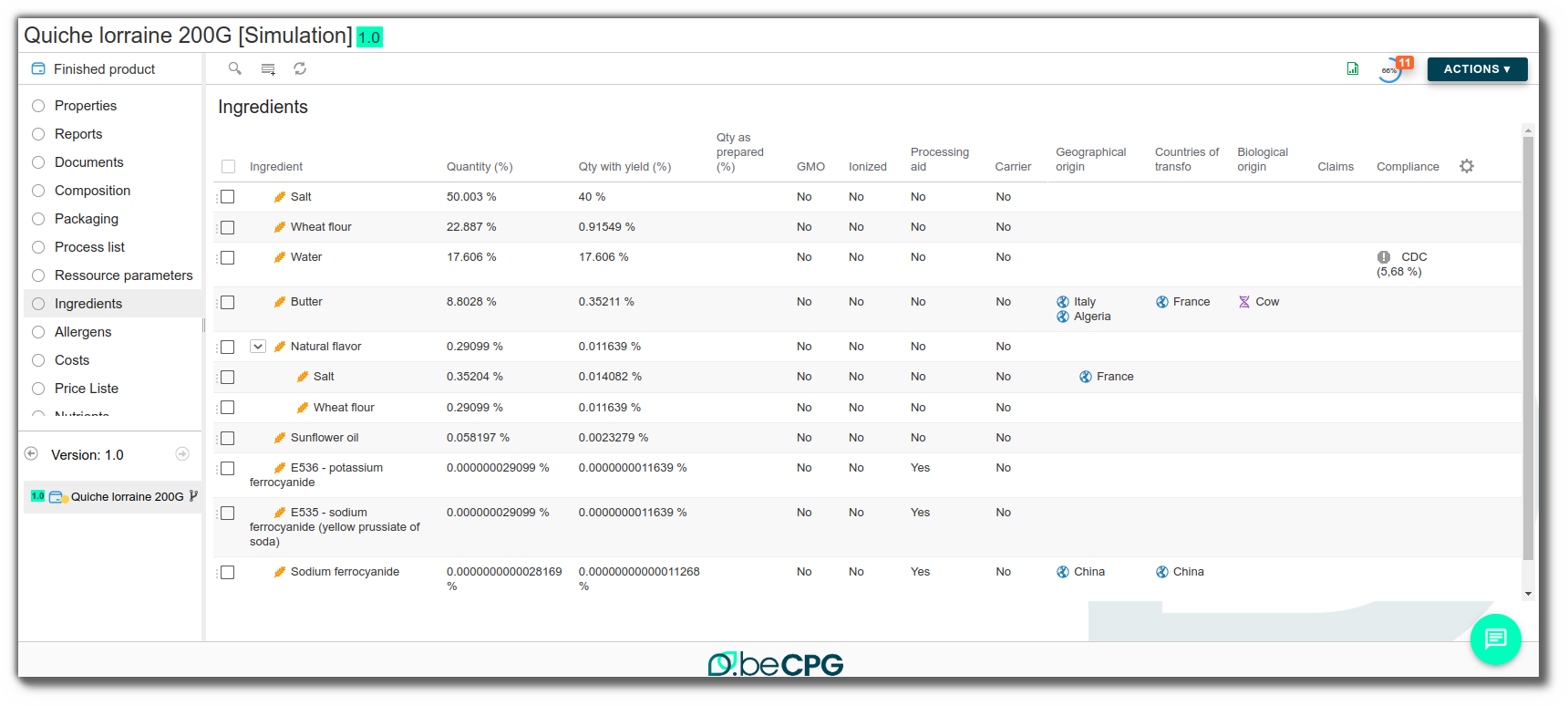
Several columns are available:
- Quantity: average quantity of the ingredient in the product
- Quantity with yield: quantity with yield and water loss taken into account
- Quantity as prepared: quantity with yield, water loss and secondary yield taken into account. Click here
- Optimization target
- Optimization result
- Conformity: linked to product specification, alerts you to the presence of a non-compliant ingredient. Click here for more information.
Note: Ingredients with identical percentages are sorted in lexicographical order. Special characters and numbers are considered before alphabetical characters. Upper case letters are considered before lower case letters. e.g. "A" comes before "a", "Sodium Acetate" (where "Acetate" begins with an uppercase "A") will be placed before "acacia" (where "acacia" begins with a lowercase "a").
Dangerous substances management
The regulation of hazardous substances is based on several legislative and regulatory texts. They are based in particular on the European regulations such as REACH. These substances, classified as CMR (carcinogenic, mutagenic, reprotoxic), endocrine disruptors or SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) must be identified and controlled throughout the product life cycle. In this context, the list of substances of concern makes it possible to monitor and analyze their presence.
Add a dangerous substance to an entity
The beCPG database includes a selection of substances to be configured as hazardous substances with their associated hazard type (carcinogenic, mutagenic, etc.), in accordance with Article 57 of the REACH regulation.
In the ingredient list
Hazardous substances can be managed directly in the list of ingredients. This is a fairly common situation, particularly in cosmetics, where certain ingredients can be classified as substances to be monitored. Simply add the substance as an ingredient in the raw material, and it will automatically be included in the list of dangerous substances.
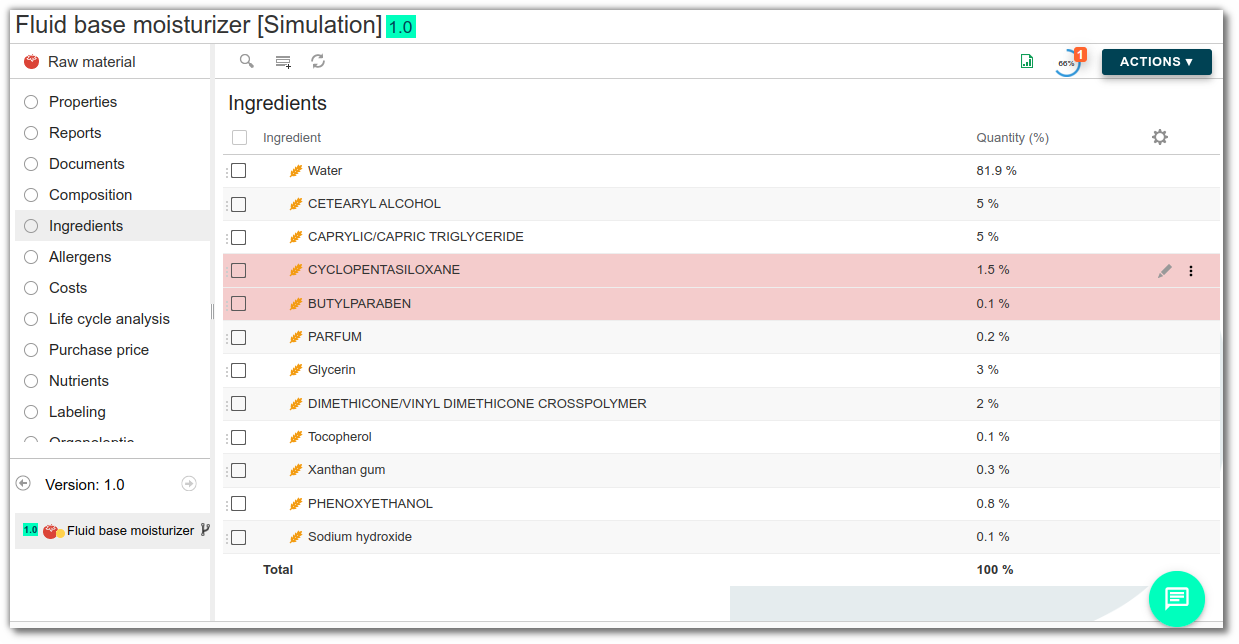
It appears automatically with the quantity used, making it easy to track its impact on finished products.
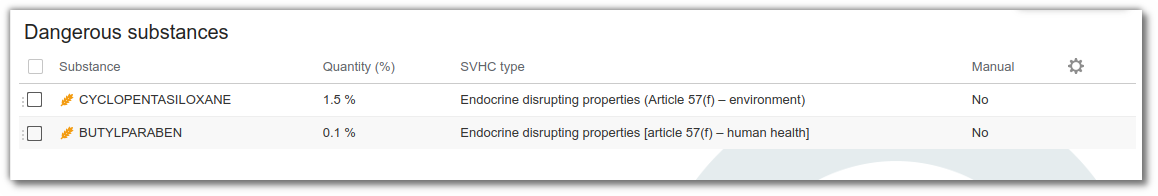
In the list of dangerous substances
It is also possible to add the substance manually to the “ dangerous substances ” list if it is not an ingredient, and to enter the quantity and migration rate for packaging (i.e. the proportion of the substance likely to pass from the material to the finished product). Management does not stop at the mere presence of the substance. The system also takes into account the migration rate, when this information is available. This gives a more accurate picture of what is actually present in the final product. This is useful for food and cosmetics products, where the impact of packaging on the formula can be real.
Indeed, certain materials used for packaging or cooking can release undesirable substances into the food. This is the case, for example, with certain plasticizers present in bottles, inks used on food jars, or fluorinated compounds (PFAS) (source: Le Monde). Bisphenol A (BPA) is also concerned, and is now the subject of European regulation (EU) 2024/3190. This regulation prohibits its use in materials in contact with foodstuffs.
Modify or create a hazardous substance
Dangerous substances are created and modified in the administration. Click here for more information.
Formulation of dangerous substances
The list of hazardous substances is compiled automatically from the raw materials and packaging used in the recipe. As soon as an ingredient or packaging contains a dangerous substance, it is automatically identified. It then appears in the list of dangerous substances for the finished product. Its name, category (CMR, SVHC, PE...) and quantity are automatically formulated.

It is also possible to display details of the origin of each substance, with a precise breakdown between the contribution of raw materials and that of packaging. This enables you to quickly see where a substance comes from and at what level it is used.
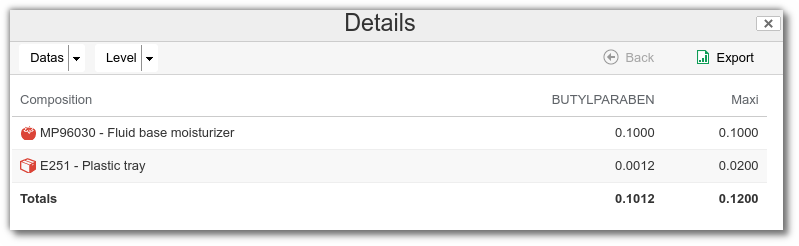 />
/>
Dangerous substance claims
In beCPG, claims are automatically calculated from the data entered. The system checks whether relevant substances are present and whether their concentration exceeds the threshold. For example, if a package contains more than 0.1% lead, it will not be possible to display the claim “SVHC-free”. However, if no such substances are detected above the threshold, the claim will be deemed to have been made.
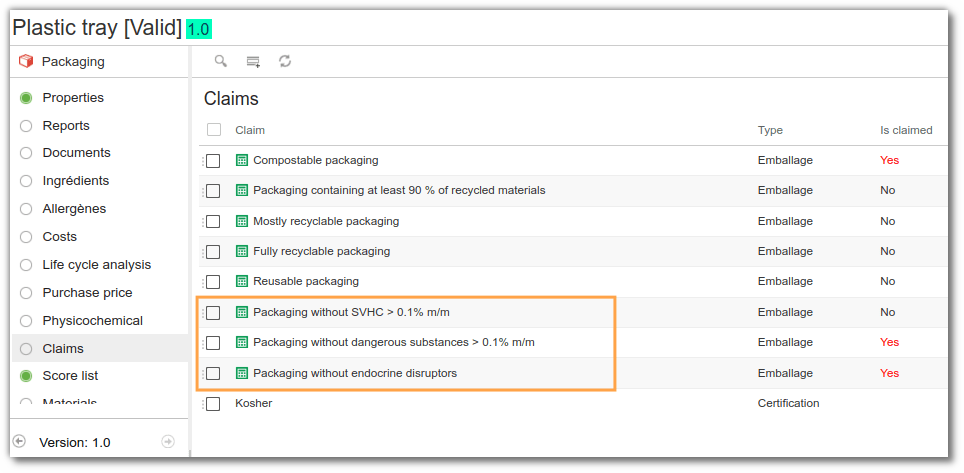
Ingredient toxicity management
The ingredient toxicology module is based on three beCPG administration lists, to be managed in this order:
- Ingredient Characteristics: using the Toxicology tab, you can enter the various toxicological data for your ingredients. For more information, click here.
- Toxicity Characteristics: For more information, click here.
- Ingredient Toxicology Characteristics: For more information, click here.
Raw Material Toxicities
The toxicities that appear depend on the ingredients present in the ingredient list. These must be present in the administration's “Ingredient Toxicology” list. The Toxicity list can be added to the raw material template so that it appears for all raw materials.
- Toxicity: the name of the toxicity appears here.
- Relative maximum quantity (%): all ingredients with the same toxicity appear here. To see which ingredients cause the toxicity, simply click on the three dots and then “Details.”
- Manual: If the percentage reported by the automatic calculation is not correct, you can modify the toxicity concerned and check the “Manual” field. In this case, even if the RM is reformulated, the manual percentage will be retained.
By default, the “Manual” field is unchecked, which allows the toxicity data reported by the system to be automatically retrieved.
It is also possible to manually add toxicities by clicking on the “Add” button. Remember to check the “Manual” field.

Toxicities of a semi-finished or finished product
The formula will calculate the “maximum relative quantity (%)” based on the toxicities present in the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that make up the semi-finished product or finished product. For a given toxicity, it is the lowest (most restrictive) percentage that is reported to the entity.
To see which ingredients contribute to the toxicity, simply click on the three dots and then “Show characteristics details”.
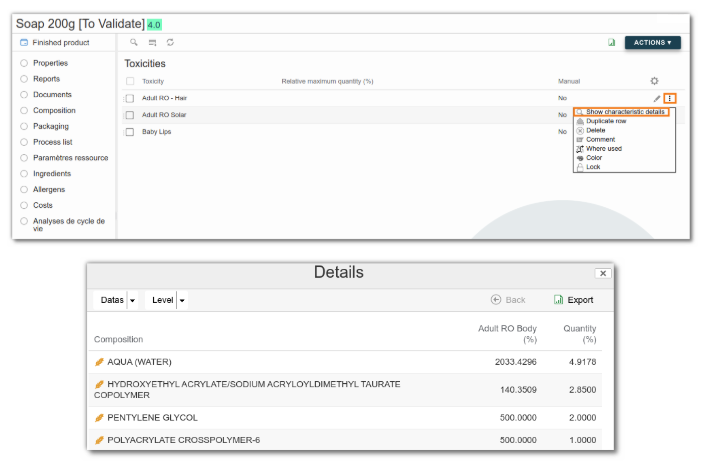
The details of the calculations are shown in the table below:
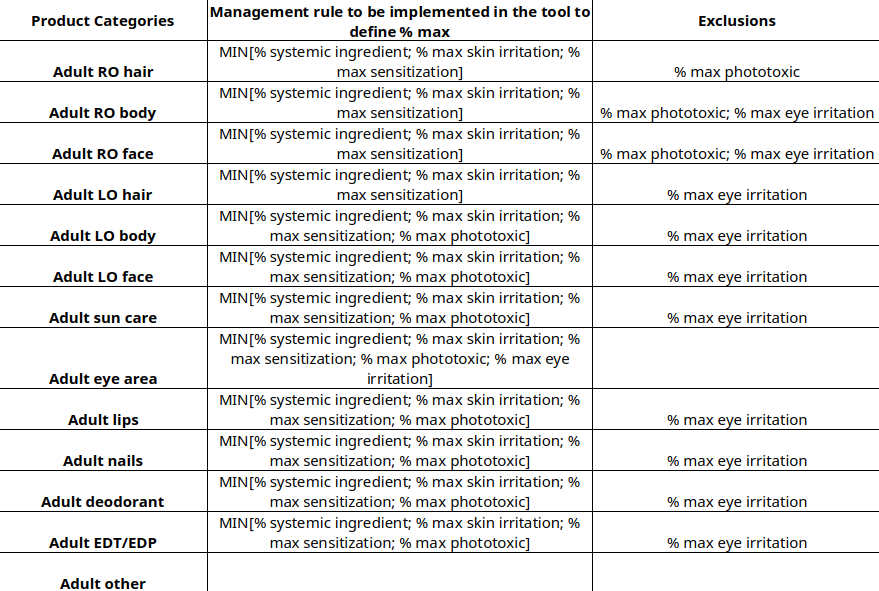 RO : rinse-off
LO : leave-on
RO : rinse-off
LO : leave-on