showToc: true
Product quality management
Control points
Control points group together the controls to be carried out.
Example: a microbiological check on receipt of a raw material may include :
- Controlling the quantity of Salmonella ;
- Checking the quantity of coagulase + Staphylococcus;
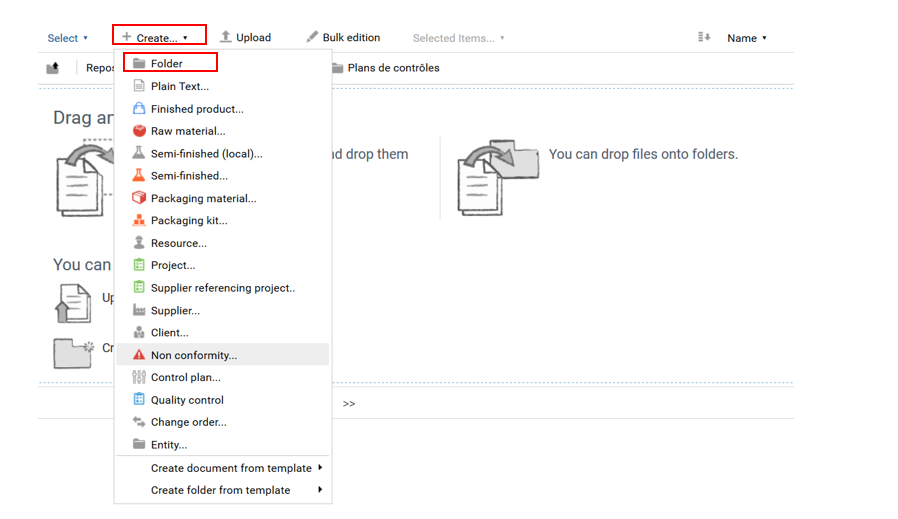
To create a control point, go to Warehouse> Quality> Specifications> Control points. Click on “Create+” and select “Folder”.
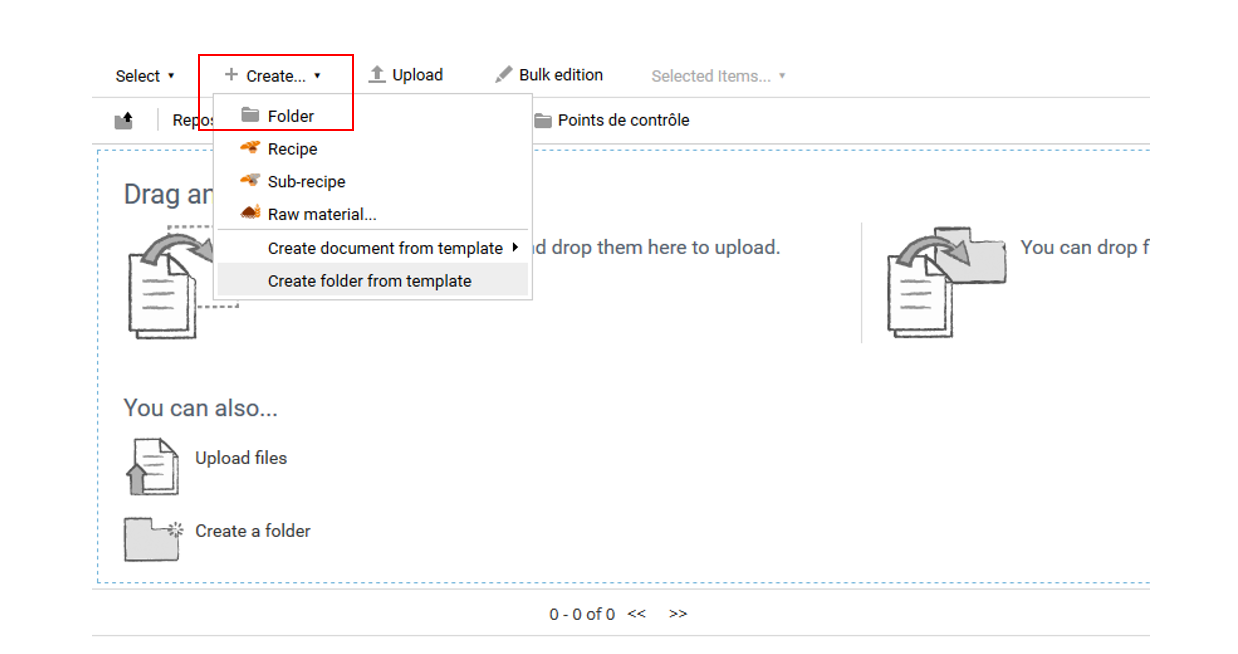
A form appears, asking you to enter the name of the control point. If this needs further explanation, the “Description” box can be filled in.
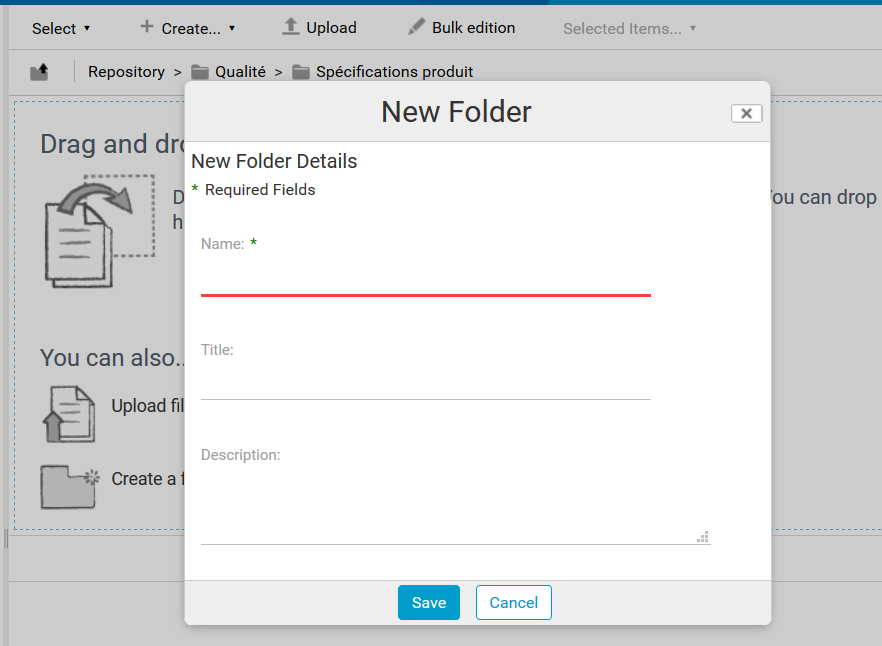
To enter the various actions to be carried out in this control point, go to the “Controls” list and click on “Add”.
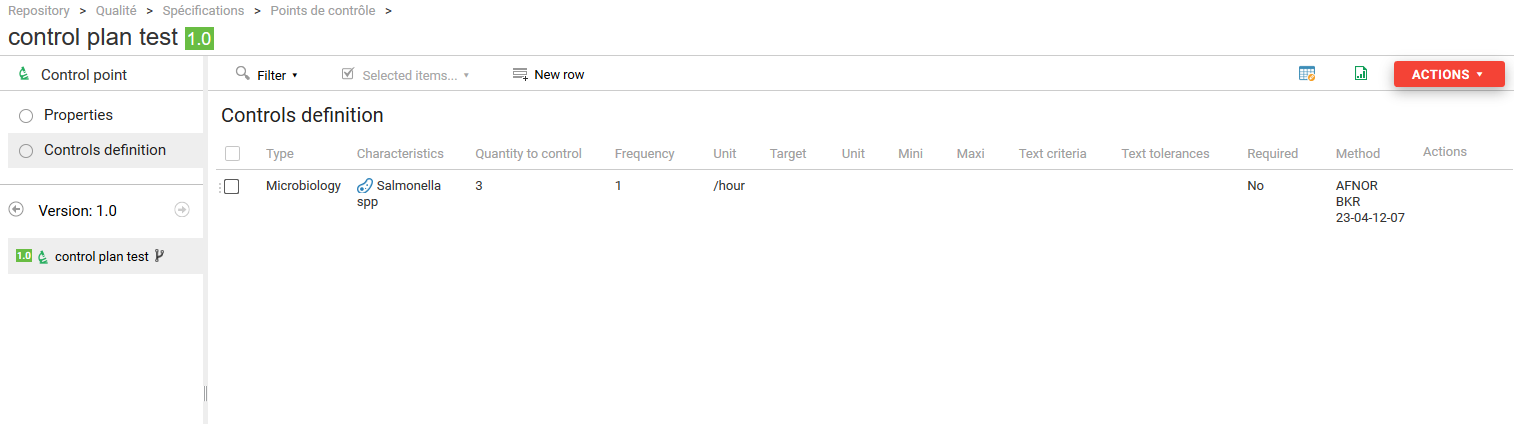
A form appears, allowing you to enter :
- type of control (microbiological, visual, physico-chemical, etc.) ;
- the characteristic to be inspected (bacteria, color, pH, etc.) ;
- the quantity to be tested (number of samples to be analyzed);
- inspection frequency ;
- the unit of this frequency;
- the target or expected quantity for the characteristic in question ;
- the unit of this target ;
- the minimum value for this target ;
- the maximum value for this target;
- a text criterion,
- a text tolerance,
- whether or not it is a final check;
- the inspection method used.
N.B.: the list of methods can be completed in the administration (beCPG> Administration beCPG> Quality lists> Control methods).
Once control points have been created, they can be used in control plans.
Control plan
Control plans are used to define all the samples to be taken in order to carry out the actions listed in the control points.
Example: on receipt of a raw material, the following checks are required:
- Visual inspection ;
- Physico-chemical inspection ;
- Microbiological control;
- Organoleptic control.
There are two ways of creating an inspection plan:
- Go to the folder where the control plan is to be created and click on “Create+” then “Control plan”.
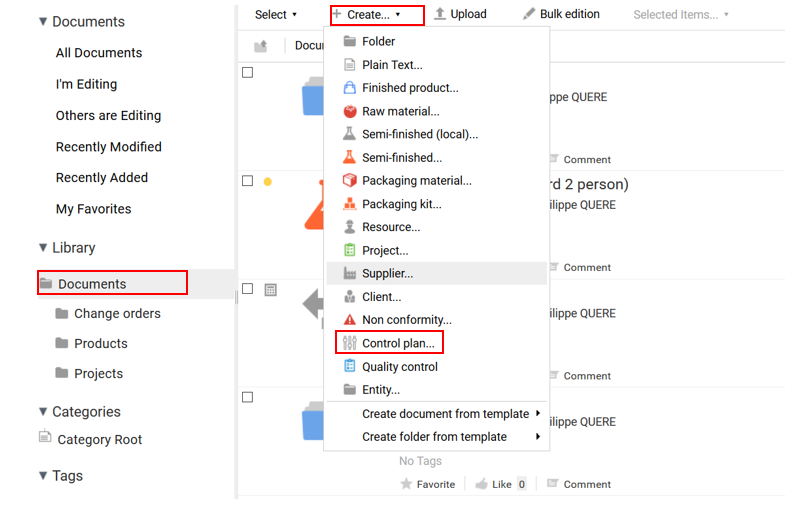
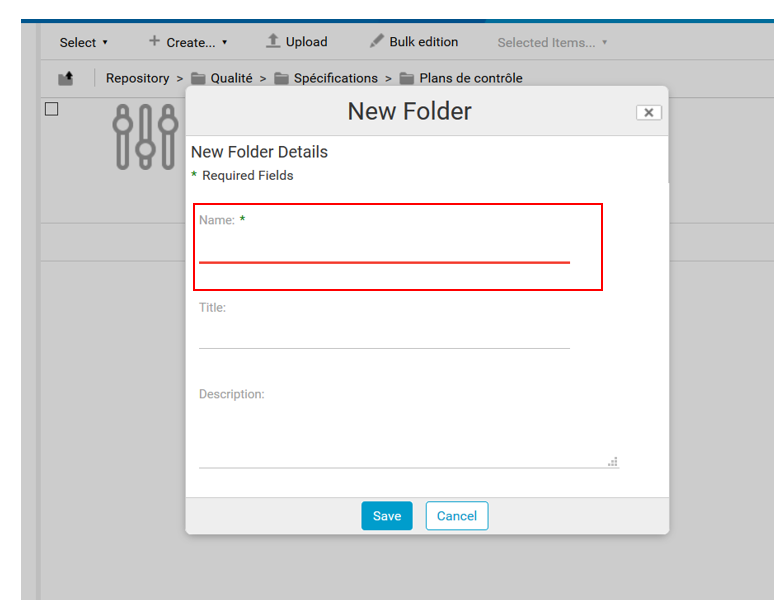
A form appears, asking you to enter the name of the control plan. If this needs further explanation, the “Description” box can be filled in.
To enter the various actions to be carried out in this control plan, go to the “Sampling” list and click on “Add”.
A form then appears, allowing you to enter :
- the control point (see “Control point” section) ;
- the quantity to be tested,
- inspection frequency,
- unit of
- the unit of this frequency ;
- the inspection stage. N.B.: the list of stages can be completed in the administration (beCPG> Administration beCPG> Quality lists> Control stages).
- sampling manager ;
- control manager ;
- correction manager ;
- a reaction.
A line appears in the samples: this is the control point to be performed.

Once the test plans have been created, they can be used for quality control.
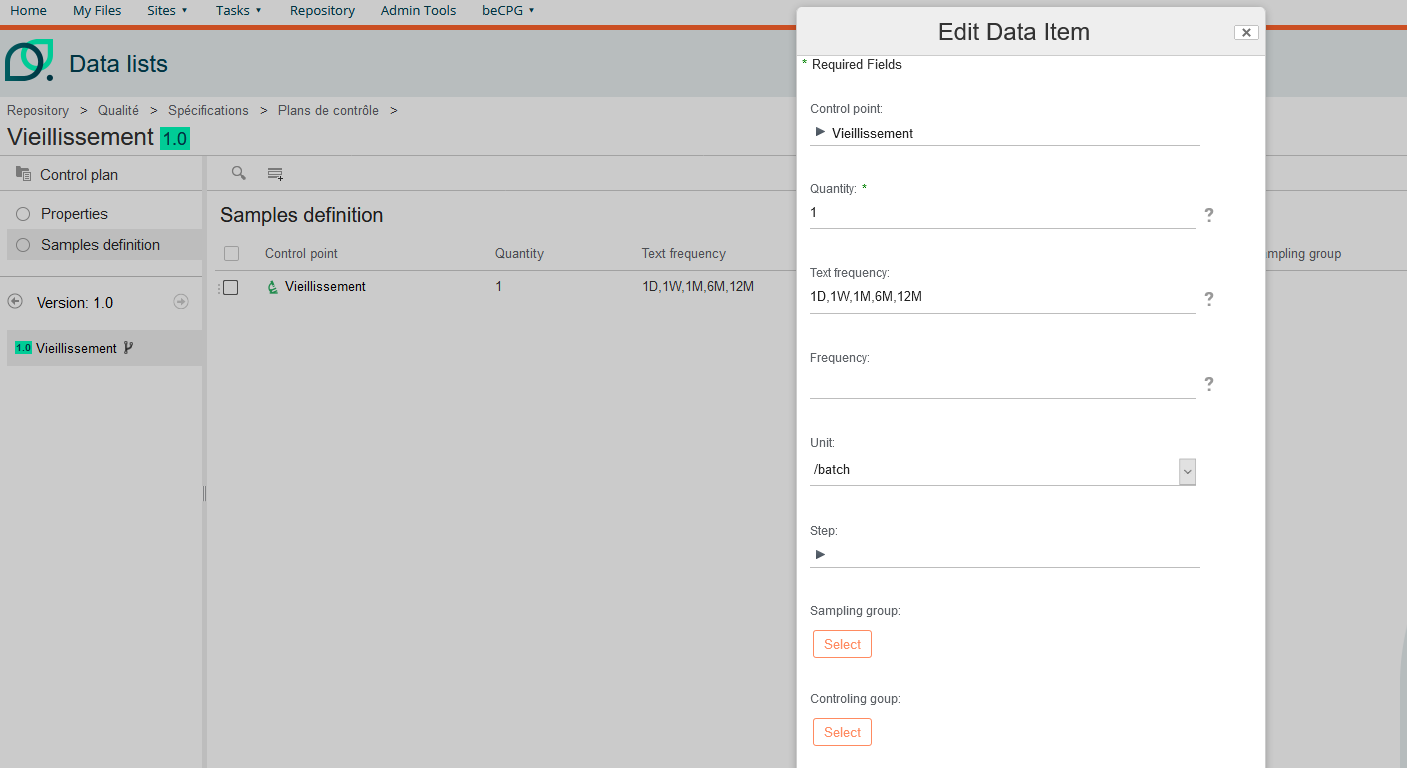
Ageing control
On the sampling list you can define the frequency.
Example :
1D,1W,1M,6M,12M
Frequencies are separated by a comma.
This corresponds to:
1 day, 1 week, 1 month, 6 months, 12 months
These frequencies correspond to the spacing of analyses after using this control plan in quality control.
From version 3.2 onwards, it is also possible to use the shelf life of the finished product to define the frequency:
BBD=DLC(J) UBD=DDM/DLUO(M) PAO=PAO(J)
Example here:
0.2BBD,0.4BBD,0.6BBD,0.8BBD,1BBD,1.2BBD
In this case, the CSD is 90J:
This corresponds to :
0.2x90J=18J , 0.4x90J=36J, 0.6x90J=54J, 0.8x90J=72J, 1x90J=90J, 1.2x90J=108J
Quality control
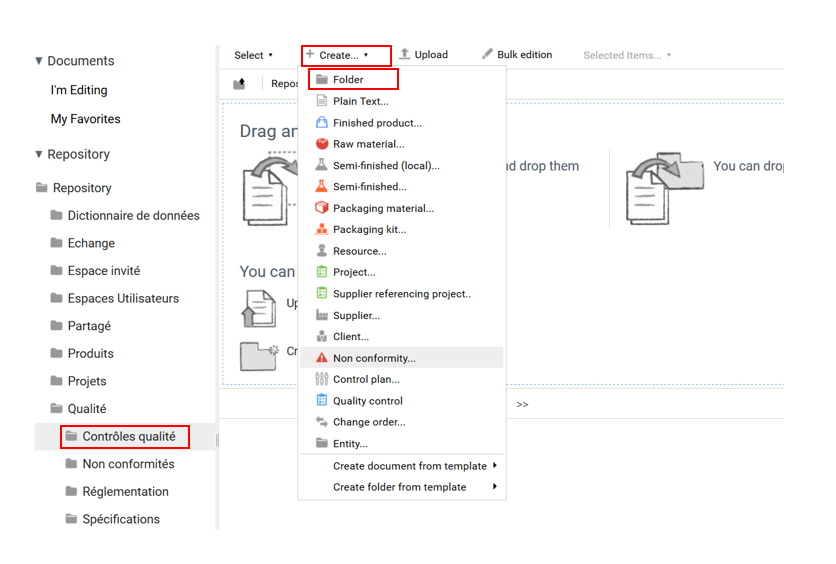
Quality controls are used to launch a control plan to be carried out on an entity (PF, SF, MP, etc.). To create a quality control, go to Entrepôt> Qualité> Contrôles qualité and click on “Créer+” then select “Dossier”.

A form appears, asking you to enter the internal name of the quality control. If it has a more formal name, the “Title” insert can be used. Similarly, if the quality control name needs further explanation, the “Description” box can be used.
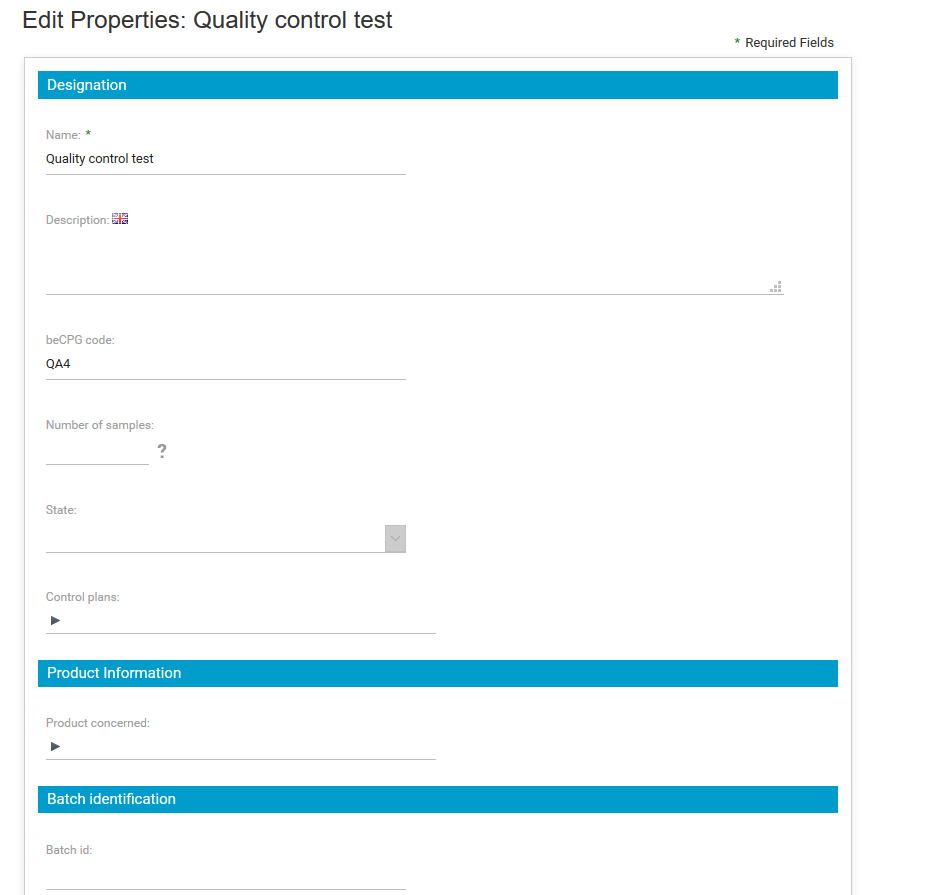
By clicking on “Edit properties”, a form appears, allowing you to enter :
- the number of samples to be tested ;
- the status;
- the control plan to be applied;
- the product concerned ;
- batch number ;
- order number;
- batch start date and duration;
- a comment.
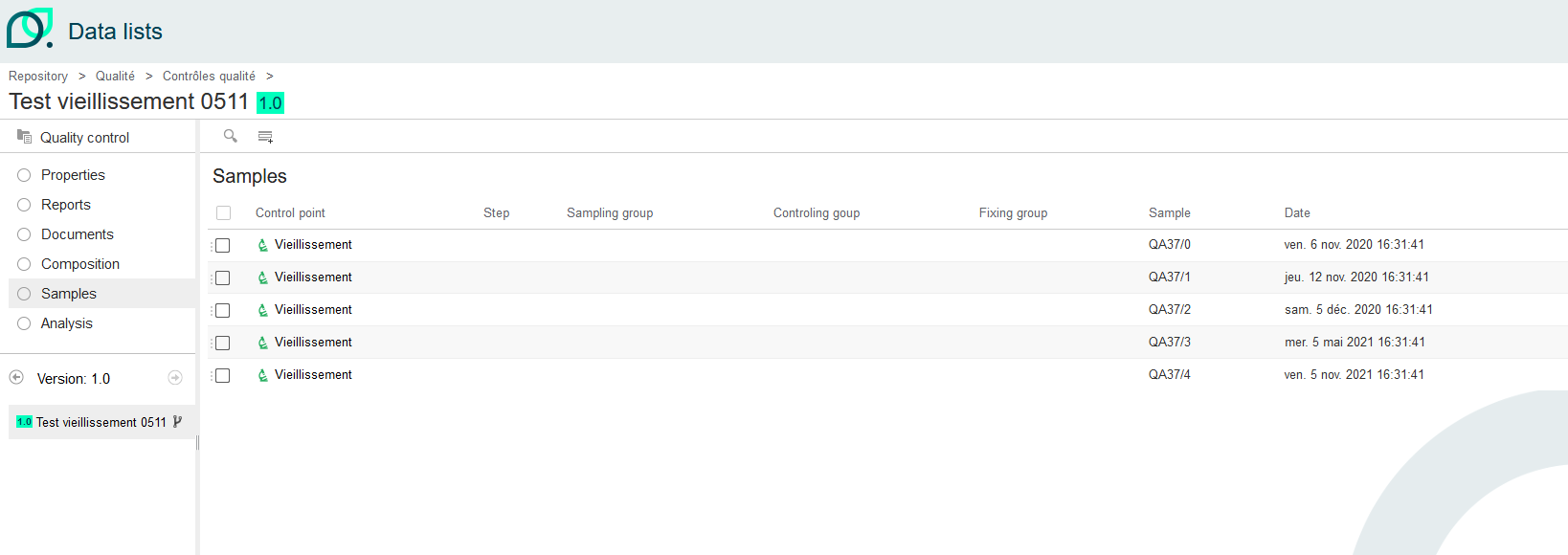
Samples
All the samples mentioned in the control plan were included in the quality control.
Analysis
By creating a quality control with a control point having frequency information, we obtain one line per frequency. The due date is calculated on the basis of this frequency and the date on which the quality control was created.
Under analysis, you'll find as many analyses to be performed as samples and frequencies configured in the control plan.
Report
Click on the “Data sheets” list to generate a product analysis report once everything has been completed.
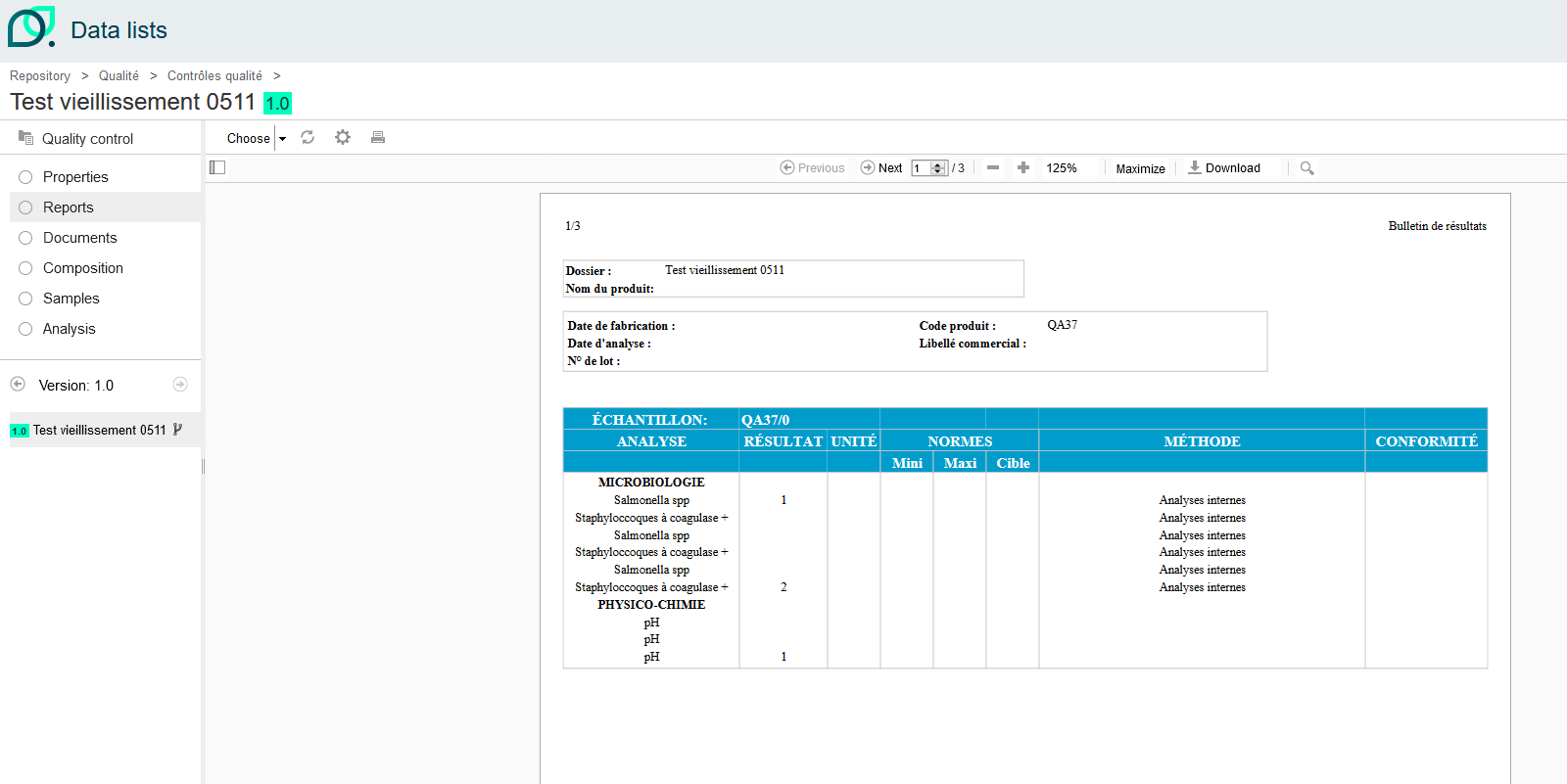
Here, in the Data Sheets section, we can generate the “Quality Control - Aging” Excel report.